- 실험소모품
- HPLC/GC column
- HPLC consumables
- Reagent
- Life Science

HPLC Consumables - Grace Vydac
- Vydac SPE Cartridge
- Vydac SPE Cartridge
- GracePure SPE
- GracePure SPE
- In-line Column PreFilter(CPF10)
- In-line Column PreFilter(CPF10)
- Carbograph SPE
- Carbograph SPE
Carbograph SPE
Introduction
Carbograph solid-phase extraction (SPE) packing is a homogenous, non-porous, graphitized carbon black (GCB) with a surface area of 100m2/g and a particle size range of 38-125μm. The primary retention mechanism is reversed-phase, but under certain conditions cationic areas of the carbon surface will act as anion exchange sites. This mixed-mode characteristic allows for the separation of acidic compounds from basic and neutral compounds.Tube Formats
Alltech offers Carbograph in both Extract-Clean and Ultra-Clean syringe barrel formats. Extract-Clean tubes consist of a polypropylene tube body and use 20μm polyethylene frits to retain the Carbograph bed. Ultra-Clean tubes consist of a fluorinated polypropylene tube body, giving the tubes the inertness of PTFE, and 10μm PTFE frits. The 10μm PTFE frits make Ultra-Clean flowrates somewhat slower than Extract-Clean flowrates.Flowrate
Carbograph is strongly retentive for non-polar compounds. This characteristic along with its non-porous surface allows the use of fast sample flowrates through a Carbograph tube, a necessary feature when processing 100mL - 1L samples. Flowrates of 20-100mL/min. are common with vacuum manifolds using up to 20 in. Hg vacuums. Flowrates up to 160mL/min are reported.1,2Elution Solvents
Since Carbograph is somewhat more retentive for organic compounds than reversed phases, generally stronger (less polar) solvents are required for elution. Solvents like methanol or acetonitrile, which are often effective elution solvents with C18, elute compounds from Carbograph incompletely or as a broad band, requiring large volumes. Common elution solvents include acetone, petroleum ether/toluene (1:1), and methylene chloride/methanol mixes (80:20). Elution solvents are modified with acid or base when separating acidic from basic and neutral compounds.1,5 Generally, 5-10mL of solvent is required for elution.General Extraction Protocol
300mg Bed SizeConditioning: Use Flowrates of 5-10mL/min.
1.Pass 5mL of methylene chloride:methanol (80:20) through the packing bed.
2.Pass 2mL of methanol through the packing bed.
3.Pass 5mL of deionized water, adjusted to pH2 with HCl, through thepacking bed.
Sample Application
1.Pass the sample through the packing bed at a flowrate of 20-100mL/min.Tube Wash: Use Flowrate of 5-10mL/min.
1.Wash the tube with 5mL of deionized water.2.Dry the tube by passing air through the tube for 2-5 minutes.
Elution: Use 5mL/min Flowrate
1.Elute basic and neutral compounds with 1mL of methanol followedby 5mL of methylene chloride:methanol 80:20.2.Elute acidic compounds with 5mL of 80:20 methylene chloride:methanol containing 0.02M TMAOH.
3.Reduce volume of extract and reconstitute with appropriate solventfor analysis.
Applications
Carbograph is effective at extracting a broad range of compounds. Its use has been reported in the literature for the extraction of pesticides and herbicides,1,2,4,5,6,7 phenols,3,8 analines,9 surfactants,10,11 priority pollutants,12 estrogens,13 and antidepressants.14 Carbograph’s mixed mode properties will separate a broad range of pesticides and herbicides.1,5Typical chromatograms of acidic and basic/neutral pesticides and herbicides (from Reference 1) are shown in Figure 1. Recoveries for these compounds at the low μg/L level are over 90%. Carbograph is more retentive for polar compounds in aqueous matrices than other reversed phases. Generally, a 1 gram packing bed is required for adequate retention of the most polar compounds. Phenols3 and polar pesticides4 are two classes of polar compounds that are effectively extracted from water at low μg/L concentrations. Table 1 compares recoveries of phenols, and Table 2 polar pesticides, extracted with Carbograph and C18 tubes.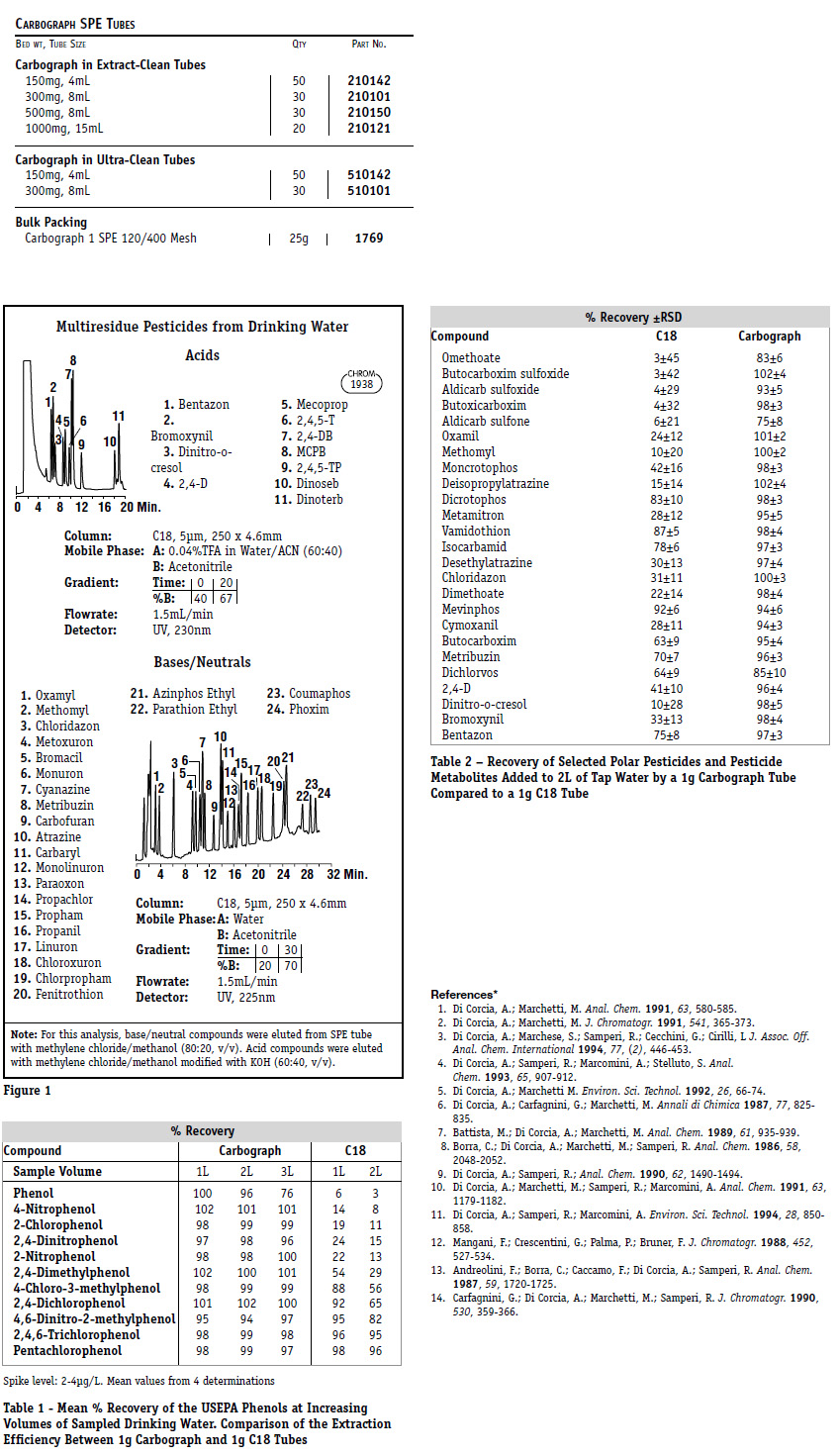

경기도 수원시 장안구 장안로496번길 93(이목동) 2층 (주)충인과학 대표전화 : 031.241.6413 FAX : 031.241.6424
COPYRIGHT 2015 CHOONGIN ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
COPYRIGHT 2015 CHOONGIN ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.

 Home > 실험소모품 > HPLC Consumables > Grace Vydac > VYDAC SPE Cartridges
Home > 실험소모품 > HPLC Consumables > Grace Vydac > VYDAC SPE Cartridges